What Is Business Analytics? In-Depth Guide

Businesses are inundated with data. To convert this raw data into valuable insights, organizations rely on business analytics. Business analytics has become a crucial tool for organizations aiming to leverage data to make strategic decisions, improve operations, and maintain a competitive edge in their industries. As organizations embrace digital transformation, business analytics will expand, shaping the future of how businesses operate in a data-centric world.
What Is Business Analytics?
At its core, business analytics involves the use of statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and data mining to identify trends, patterns, and correlations within complex data sets. By extracting meaningful insights from raw data, businesses can uncover hidden opportunities, mitigate risks, and make informed decisions that are backed by evidence rather than intuition.
Defining Business Analytics
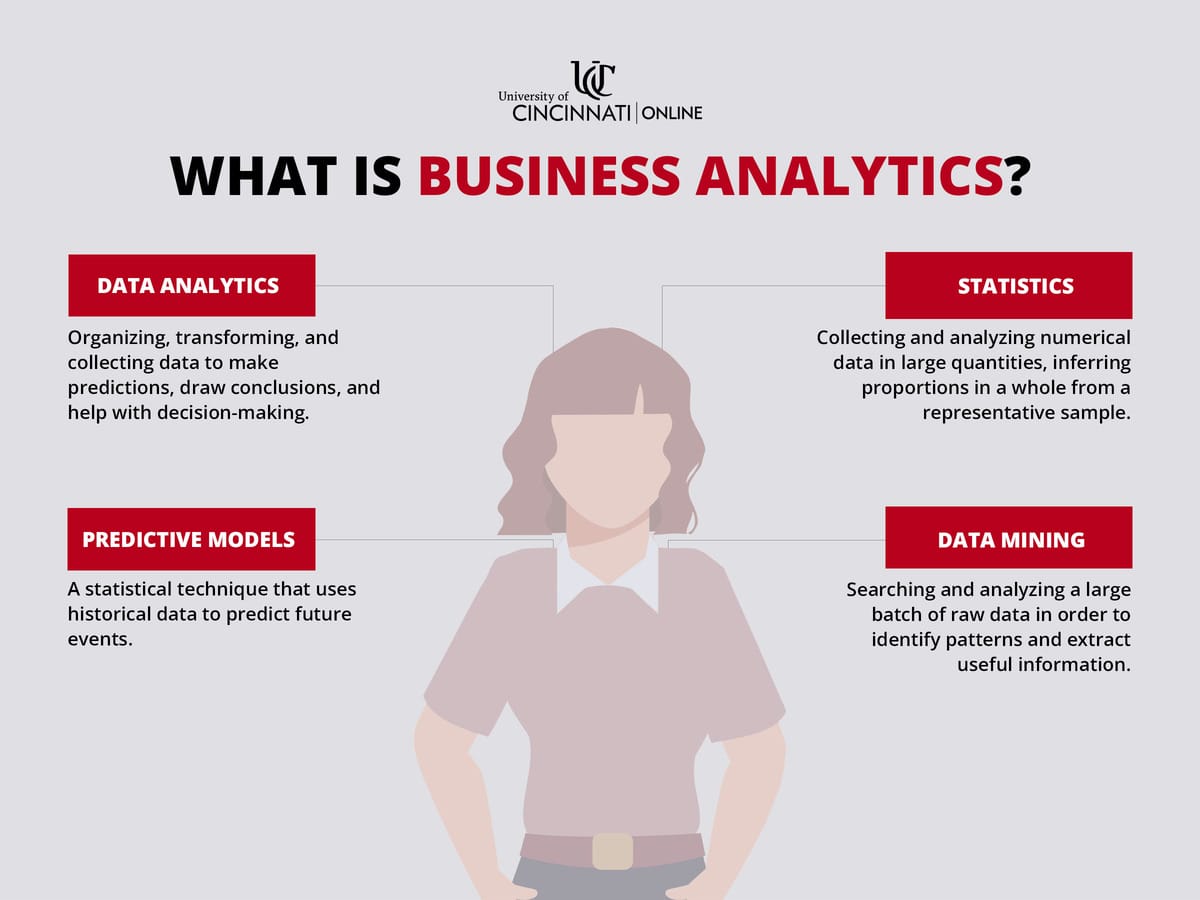
Business analytics involves the use of data analysis, statistics, and predictive models to help businesses make better decisions. It uses a variety of methods and tools to examine data, enabling organizations to learn from the past, predict future events, and improve their operations. For instance, imagine a clothing store that wants to better understand which items sell the most during different seasons. To do this, the store may analyze past sales data to identify trends, use statistical methods to determine the reasons behind varying sales numbers, and employ predictive models to estimate the stock required for the next season.
Components of Business Analytics
Business analytics includes a variety of methods that organizations use to analyze data for improved decision-making. These methods can be categorized into three main components: Descriptive Analytics, Predictive Analytics, and Prescriptive Analytics. Each of these components plays a crucial role in extracting insights from data to drive strategic decisions and improve operational efficiency. Descriptive Analytics: This component focuses on summarizing historical data to understand past events and trends. Techniques like data aggregation and data mining are used to uncover patterns that can provide valuable insights. For instance, retail companies utilize descriptive analytics to analyze sales data and gain insights into consumer behavior. By identifying which products sell best during specific times, businesses can tailor marketing strategies to target customers more effectively. Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics uses statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future trends and behaviors based on historical data patterns. Financial institutions employ predictive analytics to assess credit risk and predict customer churn. By analyzing past financial behaviors, these institutions can proactively manage risks and personalize customer experiences, ultimately improving customer retention and satisfaction. Prescriptive Analytics: This advanced component goes beyond predicting future outcomes to recommend actions that can optimize results. It uses optimization and simulation techniques to simulate different scenarios and predict the impact of various strategies. Healthcare providers may use prescriptive analytics to optimize patient scheduling and allocate resources efficiently. By analyzing patient data and operational variables, hospitals can enhance both patient care and operational efficiency.
Tools and Techniques in Business Analytics
Business analytics is a field that relies on sophisticated tools to transform raw data into valuable insights. These tools help organizations visualize trends, understand patterns, and make data-driven decisions with confidence. Here’s a closer look at some of the key tools and technologies that drive business analytics:

Why Is Business Analytics Important?
Business analytics plays a pivotal role in helping organizations maintain competitiveness in today’s data-driven landscape. By harnessing the power of data, companies can achieve several strategic advantages: Improved Efficiency: Business analytics enables organizations to pinpoint inefficiencies in processes through data analysis, facilitating streamlined operations and reduced costs. By identifying bottlenecks or areas for improvement, businesses can optimize resource allocation and enhance overall operational efficiency. Enhanced Customer Understanding: Analyzing customer data provides invaluable insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and buying patterns. This deeper understanding allows businesses to personalize their offerings, improve marketing strategies, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, retail companies can use analytics to segment customers based on purchasing habits and tailor promotions accordingly. Competitive Advantage: Businesses that effectively leverage business analytics gain a significant competitive edge by making data-driven decisions swiftly and accurately. By identifying market trends and emerging opportunities early on, organizations can proactively adjust strategies, innovate product offerings, and seize new growth opportunities ahead of competitors. This agility in decision-making is crucial in dynamic markets where staying ahead of the curve can determine long-term success. Business analytics empowers organizations to not only optimize their internal operations and understand their customers better but also to strategically position themselves in the marketplace, driving growth and maintaining a competitive edge.
Common Business Analytics Careers
A career in business analytics can be both rewarding and dynamic. Here are some common roles:
- Business Analyst: Focuses on improving business processes through data analysis.
- Data Analyst: Analyzes data to provide actionable insights.
- Data Scientist: Uses advanced analytics, including AI and machine learning, to solve complex problems.
- Data Engineer: Builds and maintains data infrastructure and pipelines.
Business Analytics Trends and Outlook
The field of business analytics is continually evolving with advancements in technology. Some current trends include: Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is increasingly being integrated into business analytics for predictive and prescriptive analytics. Big Data: As the amount of data generated continues to grow, businesses are leveraging big data technologies to handle and analyze large datasets. Data Visualization: Tools that provide visual representations of data are becoming more sophisticated, making it easier for decision-makers to interpret complex data.
Skills Needed for a Career in Business Analytics
To excel in the field of business analytics, individuals must possess a blend of technical proficiency and essential soft skills, all of which are emphasized in the business school curriculum at Lindner College of Business:
UC's MS in Business Analytics Program Can Advance Your Career
The University of Cincinnati’s online Master of Science in Business Analytics program at the Carl H. Lindner College of Business is nationally recognized and has a proven track record of placing students in successful, high-profile companies. Predictive Analytics Today has named the University of Cincinnati the No.1 MS Data Science school in the country, and Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) ranked it 18th globally and 7th nationally among U.S. public universities. Graduates from the MS in Business Analytics program at the University of Cincinnati have found placements in leading companies such as Fifth Third Bank, NBC Universal, Procter & Gamble, Tiger Analytics, Amazon, Capital One, PayPal, and Tesla. The program’s strong reputation and comprehensive training prepare students for high-demand roles in the business analytics field. Moreover, Fortune has ranked it #3 among the best online master's in business analytics programs in 2024, further underscoring its excellence and the opportunities it provides to its graduates. The program offers a comprehensive curriculum designed to provide expertise in descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. It is tailored for working professionals, with a part-time format that can be completed in one to two years. The 33-41 credit hour program is delivered entirely online with asynchronous courses, allowing students to balance their studies with personal and professional commitments. Students benefit from learning under experienced faculty from the Lindner College of Business who bring real-world insights into the classroom. Additionally, every student is assigned a dedicated Academic Advisor and a Student Success Coordinator, offering one-on-one support from start to graduation. This ensures that students receive the guidance they need to manage their time effectively and meet all degree requirements.
Take the Next Step Toward Your Master’s Degree in Business Analytics
If you’re ready to explore the career opportunities that await you with an MS in Business Analytics degree, call our Enrollment Services Advisors at (833) 347-5495. They can answer your questions about the master’s program, explain tuition and financial aid or tell you about our long-standing commitment to military-affiliated students (i.e., active-duty military, members of the National Guard and the Reserves, veterans and their families).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is business analytics (in simple terms)?
Business analytics is the process of using data analysis and statistical methods to make better business decisions. It involves looking at past data to understand what happened, predicting future trends, and figuring out the best actions to take. By doing this, businesses can improve their operations, understand their customers better, and stay ahead of their competitors.
Is business analytics a good career?
Acquiring skills in business analytics could be a wise move. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the demand for business analysts is expected to increase by 36% in the next decade. The University of Cincinnati offers a Master of Science in Business Analytics with an average graduate salary of $106,318, job placement rate of above 95 percent, and flexible online classes built for part-time students. Our Lindner College of Business Graduates pursue roles such as data scientists, consultants, market analysts, and more, and have landed jobs at prestigious companies such as Fifth Third Bank, NBC Universal, and Amazon.